Sustainability is taking its seat in the boardroom, leading the demand for standardizing ESG solutions that deliver real and valuable impact. As discussed in our previous article, ISSB, or the International Sustainability Standards Board, is a global standard-setting body that aims to develop and promote a comprehensive global baseline for sustainability-related financial disclosures.
The ISSB was established to enable the creation of global sustainability standards. It seeks to fill the apparent gaps in standardization within sustainability reporting and position itself to create more efficient accountability measures for companies and their investors.
As climate transparency rules become more standardized, forward-thinking companies are preparing to integrate these requirements into their operations. While the U.S. has taken a more gradual approach compared to regions like the EU, there is growing momentum toward stronger regulatory frameworks. Companies that proactively adopt ISSB reporting standards will be better positioned to meet future expectations and gain a competitive edge.
What is the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB)? A recap
The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) is an independent, private-sector body dedicated to developing and approving Sustainability Disclosure Standards (IFRS SDS). Operating under the oversight of the IFRS Foundation, the ISSB sets global standards for sustainability financial information disclosure.
The primary goal of the ISSB is to provide companies with clear guidance on sustainability disclosure, enabling them to offer high-quality, transparent, and comparable information to investors and other stakeholders.
What are the IFRS sustainability disclosure standards?
The IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards, developed by the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), provide a global framework for reporting sustainability-related risks and opportunities. Established under the IFRS Foundation, these standards provide a common language for delivering consistent, comparable information that investors can use to assess how sustainability issues affect enterprise value.
The first two standards—IFRS S1 and IFRS S2—set the baseline. IFRS S1 covers two main types of general sustainability disclosures, while IFRS S2 focuses specifically on climate-related risks and opportunities. Both are designed to align with existing frameworks like the TCFD, requiring companies to report on governance, strategy, risk management, and performance metrics.
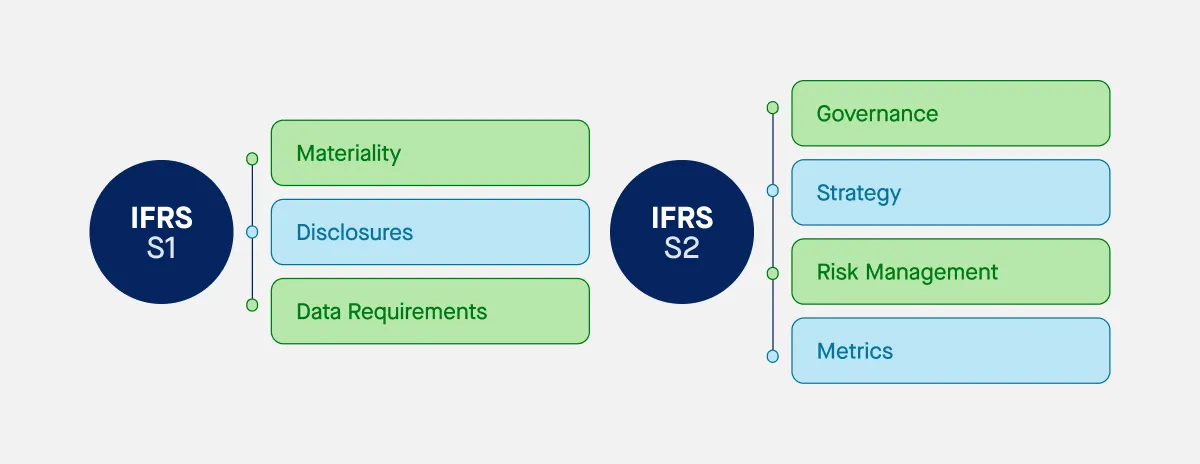
The IFRS framework helps businesses prepare for a global shift toward transparent, investor-focused sustainability reporting.
Why does ESG standardization matter more than ever?
ESG reporting resembles alphabet soup: SASB, GRI, CDP, etc. There are many choices, but no clear solution regarding the best path. Furthermore, there has long been no all-encompassing approach to it. It is a complex landscape to navigate, and it becomes more about figuring out how to puzzle together the frameworks offered to fit the desired reporting outcomes. Within these frameworks, companies find overlap in their efforts or unclear benchmarks, heightening skepticism among investors.
In the US, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is pushing to create the rules and guidelines that companies must follow within the ESG realm. However, 70% of business leaders report they are not waiting for the SEC to finalize the climate disclosure rules and will proceed with compliance regardless of when they become US law.
These statistics show just how critical the adoption of ESG standards has become across the business landscape. Furthermore, 68% of executives report their company already uses digital software for ESG reporting, 85% are concerned their company does not have the right technology in place to support the level of reporting required in the proposed rules, despite almost all anticipating it will play an essential role in meeting potential new requirements.
ISSB shines in this aspect. ISSB standards build and combine much of what other frameworks offer into one end-to-end solution.
What to look for when searching for software to support ISSB reporting
Here are the services, features and resources to keep an eye out for.
1. Full-scope emissions coverage
ISSB-aligned platforms should support comprehensive greenhouse gas emissions tracking—across Scope 1, 2, and 3. The services offered should include the ability to handle indirect emissions and integrate data from suppliers and partners across the value chain. In doing so, they should also be cost effective.
2. IFRS S1 and S2 alignment
Ensure the software is built with IFRS S1 and S2 in mind. This includes functionality for reporting on governance, strategy, risk management, performance metrics, and key concepts related to sustainability and climate risk.
3. Automated workflows and data integration
Automated data collection and processing are key to reducing reporting errors and easing the administrative burden. Look for tools that connect seamlessly with your existing systems and streamline emissions data gathering, calculations, and validation – including sustainability related financial information.
4. Scenario analysis and forecasting
Effective software should include tools for modeling physical and transition risks under different climate scenarios. This supports forward-looking disclosures in line with IFRS S2 and helps inform strategic decision-making processes .
5. Real-time reporting and audit readiness
Audit-ready outputs, version control, and real-time dashboards are essential for transparency and traceability. The software should make it easy to generate publicly disclosed, investor-grade reports.
6. Collaboration and connected reporting
Look for platforms that enable knowledge sharing across departments—such as finance, sustainability, and risk. Features like shared dashboards and role-based permissions can streamline workflow and reporting responsibilities.
7. Supplier engagement and benchmarking
Platforms that support supplier engagement and provide access to industry average data help enhance Scope 3 accuracy and support comparability. Benchmarking tools also allow you to gauge performance against peers and industry standards.
1. Sweep
Why it stands out:
Sweep turns sustainability management into a value driver, integrating supply chain data and audit-ready workflows to help meet IFRS expectations.
Key features:
- Real-time emissions dashboards covering all scopes
- Automated workflows to streamline IFRS-aligned disclosures
- Supplier engagement tools to track Scope 3 data
- Exportable, audit-ready reports with traceable data sources
Why it stands out:
Persefoni offers a purpose-built solution for ISSB-aligned reporting, supporting robust emissions data collection and financial risk disclosures across global frameworks.
Key features:
- AI-driven emissions calculations across Scope 1, 2, and 3
- Scenario analysis and climate risk modeling aligned with IFRS S2
- Reports aligned with TCFD, GHG Protocol, and ISSB standards
- Regulatory intelligence for staying current with global disclosure mandates
Why it stands out:
Built to scale with enterprise needs, Microsoft’s platform centralizes sustainability metrics and ensures interoperability with key disclosure frameworks like the ISSB.
Key features:
- End-to-end tracking of Scope 1–3 emissions
- Integration with Microsoft Sustainability Manager for IFRS-aligned performance tracking
- Risk and opportunity assessment tools in line with IFRS S2
- Centralized, audit-ready reporting for internal and public disclosure
Why it stands out:
IBM’s suite provides climate risk modeling and advanced emissions tracking that support both IFRS S1 and S2 requirements.
Key features:
- AI-powered emissions inventory and indirect emissions insights
- Event forecasting and physical risk modeling for climate resilience
- Industry average data benchmarking across value chains
- Customizable dashboards and reporting workflows
Why it stands out:
Workiva unifies financial and ESG data, helping companies meet investor-grade ISSB reporting expectations with full traceability.
Key features:
- Integrated platform for emissions and risk disclosures
- IFRS S1/S2-aligned workflows with traceability and version control
- Support for cross-team collaboration and audit readiness
- Compliance with global frameworks, including TCFD and CSRD
Why it stands out:
Watershed specializes in forward-looking climate data, ideal for organizations adopting IFRS S2’s scenario-based reporting approach.
Key features:
- Climate risk tools and real-time emissions forecasting
- Tailored dashboards for strategy and risk communication
- Supply chain emissions tracking across all scopes
- Built-in alignment with TCFD, ISSB, and net-zero targets
Why it stands out:
Greenly provides an accessible platform for companies at different stages of ISSB reporting readiness, with automation and collaboration at its core.
Key features:
- Streamlined emissions data collection and reporting across all scopes
- Risk quantification tools aligned with climate disclosure norms
- Collaborative features for cross-functional reporting teams
- Customizable outputs to match ISSB and investor reporting needs
Building a smarter work plan for ISSB reporting
Leading platforms like Sweep, Persefoni, and IBM offer powerful services and features that support companies in implementing ISSB-aligned disclosures. From automated data workflows to real-time risk modeling, these tools help organizations streamline sustainability reporting and drive value. Now is the time to explore the right solutions and integrate them into a practical work plan for compliance and competitive advantage.
For further information on how to select the best software for your business, read our dedicated guide.