Carbon accounting software has become a mission-critical component of modern business operations as regulatory requirements, climate disclosure obligations, and stakeholder scrutiny intensify. As greenhouse gas emissions reporting continues its transition from voluntary sustainability efforts to regulated corporate reporting, organizations need reliable, scalable tools to accurately measure, manage, and report carbon emissions across global operations and complex supply chains.
In 2026, carbon accounting software is no longer optional. Compliance with regulatory frameworks such as the EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), alignment with the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol), and increasing expectations from investors and employees alike mean that organizations must invest in robust, audit-ready carbon accounting solutions.
This guide explores the best carbon accounting software platforms in 2026, helping companies identify the right carbon accounting software based on data quality, emissions tracking, reporting capabilities, regulatory compliance, and long-term sustainability goals.
What is carbon accounting?
Carbon accounting, also known as greenhouse gas accounting, is the structured process of measuring, recording, and reporting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions generated by an organization’s activities. These emissions are typically reported in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO₂e) and form the basis of effective carbon management and sustainability reporting.
Most carbon accounting tools are built on internationally recognized carbon accounting standards, particularly the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, ensuring consistency in emission factors, indirect emissions treatment, and reporting processes across industries and regions.
Carbon accounting focuses on:
- Measuring greenhouse gas emissions accurately
- Ensuring reliable data, data validation, and transparency
- Supporting regulatory compliance and sustainability frameworks
Carbon management then uses this carbon accounting data to set emission reduction targets, manage unavoidable emissions, and guide decarbonisation strategies over time.
What is a corporate carbon footprint?
A corporate carbon footprint represents the total greenhouse gas emissions generated by a company’s business operations and value chain. This includes emissions from:
- Energy consumption
- Transportation and logistics
- Waste generation
- Purchased goods and services
- Supply chains and other indirect emissions
Accurate carbon footprint calculations rely on high-quality emissions data collected from multiple data sources. Carbon accounting software enables organizations to automate data collection, standardize reporting, and calculate emissions across all scopes in a centralized system—providing a reliable baseline for regulatory compliance, sustainability reporting, and Science-Based Targets (SBTi).
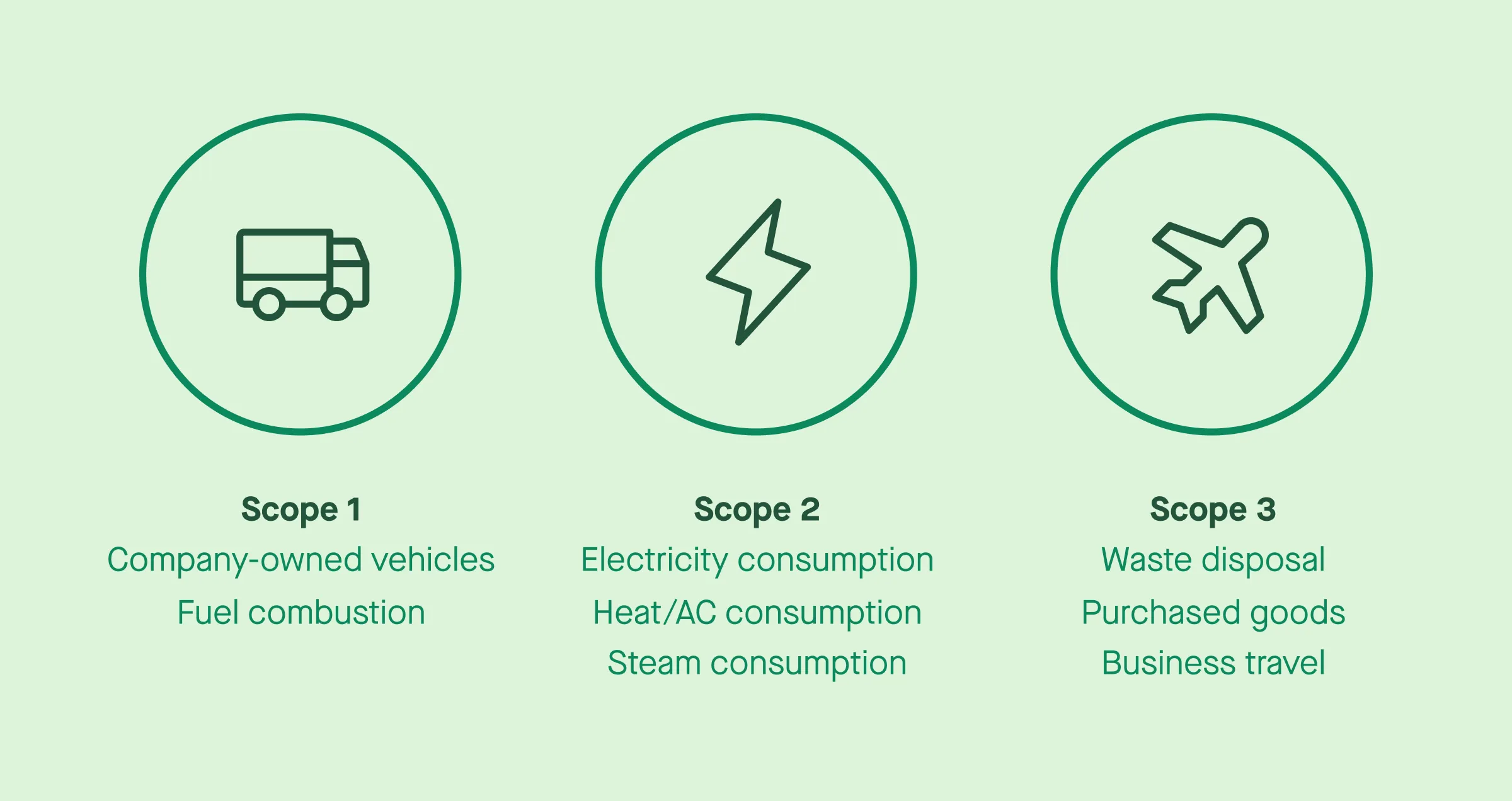
Understanding Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions
The GHG Protocol divides greenhouse gas emissions into three categories:
- Scope 1: Direct emissions from owned or controlled sources
- Scope 2: Indirect emissions from purchased electricity, heating, and cooling
- Scope 3: All other indirect emissions across the value chain, including suppliers, business travel, and product lifecycles
For most organizations, Scope 3 emissions represent the largest share of their carbon footprint. This makes advanced emissions tracking, supplier engagement, and automated data ingestion essential features of any carbon accounting platform.